Complete Guide to Burns: Types, Causes & Symptoms
When you think of burning, you might imagine being outdoors during a hot summer day. Or perhaps an image of your hand touching something too hot comes to mind. In both cases, you might feel a tingling sensation or see red bumps on the affected area.
However, burns are not limited to these experiences. They can take many different forms and have various causes. There are multiple types of burns that you need to know about if you want to prevent them or deal with them properly when they occur.
It’s important to understand what they are, how they happen, and what the best way is to treat them when they happen. Burns are almost common in everyday life and knowing how to deal with them effectively will help you manage the situation if it happens again. Keep reading for more information about all aspects of burns so that you’re prepared in the future.
What is a Burn?
A burn is an injury that occurs when your skin is exposed to heat, chemicals, electricity, radiation, or certain medical procedures. Burns often cause damage to the tissues under your skin, including muscle, blood vessels, and fat. Most burns are caused by heat or fire. They can also be caused by chemicals, electricity, ultraviolet (UV) light, or radiation. Burns can happen at work, home, or play.
They can also happen due to a medical procedure, such as when a laser is used. Burns can be either first- or second-degree burns. Second-degree burns affect the top layer of skin and the lower layer of skin and are often red and painful. Third-degree burns affect all layers of the skin, including the fat underneath the skin. Third-degree burns are extremely painful and cause blisters that are filled with liquid.
Types of Burns
1. First Degree Burns
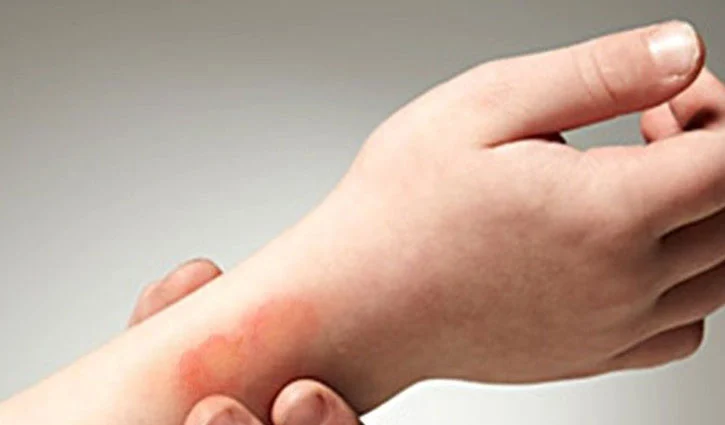
A first-degree burn is the least severe of all types of burns. It causes redness and mild swelling of the skin. It can occur when you are exposed to a hot object or substance, such as a cup of hot coffee or a skillet filled with hot oil. First-degree burns can also occur when you are out in the sun for too long without sunscreen or when the heater in your home malfunctions.
Symptoms of a first-degree burn include redness, mild swelling, and mild pain. In some cases, the skin may look white, but this is not always the case. First-degree burns can be treated by placing a cool, damp cloth on the affected area to reduce swelling and by applying moisturizer to the skin.
2. Second Degree Burns
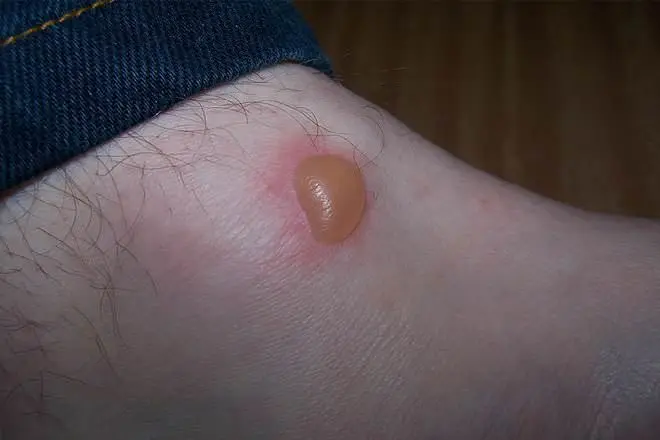
A second-degree burn causes damage to the skin’s deeper layers. It is often red and painful and may have blisters. It can occur when you are exposed to extremely hot objects or liquids, such as boiling water or a very hot pan on the stove.
Second-degree burns can also occur when you are in contact with electrical wires or when chemicals come in contact with your skin. Symptoms include redness, swelling, pain, and blisters that look like fluid-filled sacs under the skin. Second-degree burns require medical attention and may require a skin graft.
3. Third Degree Burns
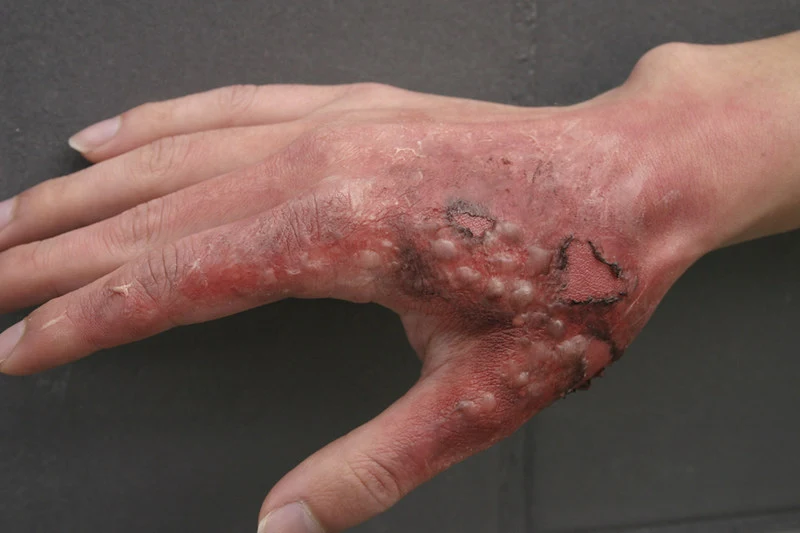
A third-degree burn causes damage to all layers of the skin, including the fat underneath the skin. It is extremely painful and may cause blisters filled with fluid. It can occur when you are in contact with extremely hot substances or objects, such as a pot of boiling water or an electrified wire.
Third-degree burns can also occur when chemicals that contain hydrofluoric acid come in contact with your skin. Third-degree burns require immediate medical attention. They can be fatal if not treated properly.
4. Fourth Degree Burns
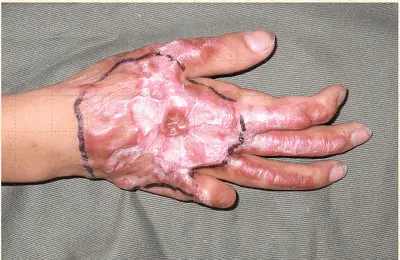
A fourth-degree burn extends beyond the skin layers and into the muscles and bones. It can occur when you are exposed to extremely hot substances or objects, such as molten metal or a very hot liquid such as boiling water. Fourth-degree burns are very painful and often lead to amputations. They require immediate medical attention and surgery.
Understanding the Basics of Burn Treatment
Burns can be treated at home by following a few basic steps. First, immediately remove any clothing or jewelry from the affected area. Second, put the burned area under cool water for at least five minutes. Be careful that the water temperature is not too cold or too hot. Third, gently clean the burned area with mild soap and water.
Fourth, apply an antibiotic cream or ointment to the area. Fifth, cover the wound with a clean bandage. Finally, follow-up with your doctor for proper treatment. If you have a serious burn, you should go to the emergency room right away.
While you are there, do not move the affected area. If your wound is deep or large, they will probably want you to stay in the hospital. Depending on the severity of the burn, you may be treated with antibiotics and pain medications. You may also receive fluids and be monitored for signs of infection. Doctors may need to remove infected or damaged tissue, and they may place a special dressing over the wound. Depending on the severity of the burn, it may take six months or longer to heal.
Types of Burns & Their Treatments
There are many different types of burns. Knowing the types of burns and what causes them will help you better understand how to prevent them from happening to you in the first place. Electrical burns – Electrical burns can happen when you come into contact with exposed wires. They can also happen if you come into contact with a current running through the water in your home.
Electrical burns cause deep tissue damage, often affecting muscles and nerves. Electrical burns require immediate medical attention and often result in amputations. Electrical burns can cause shock, which can damage your heart and kidneys.
Fire burns – Fire burns are caused by flames that touch your skin. Fire burns can be extremely painful and can cause deep tissue damage, often affecting muscles and nerves. Fire burns can be caused by an open flame, such as a candle, or by a chemical reaction, such as when gas comes in contact with an open flame. Fire burns can cause third-degree burns and may result in amputations.
Fire burns can cause smoke inhalation and carbon monoxide poisoning, which can damage your heart and lungs. – Flash burns – Flash burns are caused by very bright light, such as a flashbang used by police or a bright light, such as the sun. They can also happen when you come into contact with a laser. Flash burns cause damage to the surface of your skin, resulting in first-degree burns. They are less painful than other types of burns and can often heal within a few days.
Conclusion: Burns Treatment
Burns can happen to anyone. Knowing the types of burns and what causes them will help you better understand how to prevent them from happening to you in the first place. Burns can be treated at home by following a few basic steps. However, if you have a serious burn, you should go to the emergency room right away. Follow these tips to help you manage burns in the future.
Source –


