Cocaine: Everything You Need to Know!
These days, almost everyone is familiar with cocaine. It’s a drug that’s been around for decades, but it continues to be popular among young adults, celebrities and high-profile socialites. While it remains illegal in all 50 states, the growing popularity of cocaine has opened the door for numerous discussions on its risks and dangers. Cocaine is an extremely powerful stimulant that causes a fast but brief activation of dopamine in the brain.
Dopamine is one of our feel-good neurotransmitters, and it plays an important role in regulating our emotions, pleasure response and motivation to take action to meet needs. When we experience something rewarding (like taking a sip from our favorite coffee mug), dopamine receptors activate in order to alert us to take action again by keeping the coffee mug nearby so we can drink from it again soon.
What is Cocaine?
Cocaine is a highly addictive stimulant drug made from the coca plant leaves. Indigenous people in South America have chewed the coca plant leaves for thousands of years. Cocaine is a white powder that can be swallowed, snorted or injected. Cocaine can cause abnormal heart rhythms and seizures, and even death. Sometimes cocaine is mixed with other drugs, such as marijuana or crack.
The different forms (powder, crack and freebase) of cocaine have slightly different effects and risks. The forms of cocaine can be changed from one form to another by using different chemicals or solvents. Freebase cocaine is the most potent form of cocaine and has the fastest onset of all the different forms of cocaine.
How does it make you feel?
Cocaine produces feelings of excitement, euphoria and bliss. It also increases energy and talkativeness while decreasing appetite. Cocaine is made from the coca plant leaves, which grow in the Andes Mountains in South America. People in many parts of the world chew the coca plant leaves to relieve pain and increase energy.
Cocaine is a white powder that can be swallowed, snorted or injected. In the brain, it blocks the re-absorption of dopamine, a chemical that transmits signals between nerve cells. This boost in dopamine levels causes a high that lasts only a few minutes.
How is Cocaine Used?
Cocaine is a white powder that can be swallowed, snorted or injected. In the brain, it blocks the re-absorption of dopamine, a chemical that transmits signals between nerve cells. This boost in dopamine levels causes a high that lasts only a few minutes.
Swallowing Cocaine: This is by far the most common way of taking cocaine and is usually combined with alcohol or another drug. Swallowing cocaine gets it into your system the fastest.
Snorting Cocaine: Cocaine is rarely used alone and is usually combined with other drugs such as marijuana or crack. Snorting cocaine puts it in direct contact with the mucous membranes and blood vessels of the nose.
Injecting Cocaine: Some people choose to inject cocaine because it is more potent, lasts longer and produces a more intense high. Certain veins in the arms and legs are often used because they are closer to the heart and can receive more blood.
Side Effects of Cocaine
Cocaine is a very addictive drug and can have serious side effects. These side effects become more severe with increased use and may lead to death. Some of the most common and dangerous side effects of cocaine include
Abnormal heart rhythms: Cocaine can cause abnormal heart rhythms, and some people die from cardiac arrest because of this.
Seizures: Some people experience seizures, which can be fatal.
Paranoia: People will often experience paranoia when they do cocaine, which can result in violent behavior.
Headaches: Many people experience headaches after they use cocaine, which can be extremely painful.
Nausea and vomiting: Many people experience nausea and vomiting when they do cocaine, which can lead to dehydration.
Lung damage: Using cocaine can cause severe lung damage, which can be fatal.
Long-Term Effects of Cocaine
The long-term effects of cocaine are very negative and can lead to death. Some of the long-term effects of cocaine use include
1. Drug addiction
Many people who use cocaine become addicted to it because of its highly addictive nature.
2. Heart problems
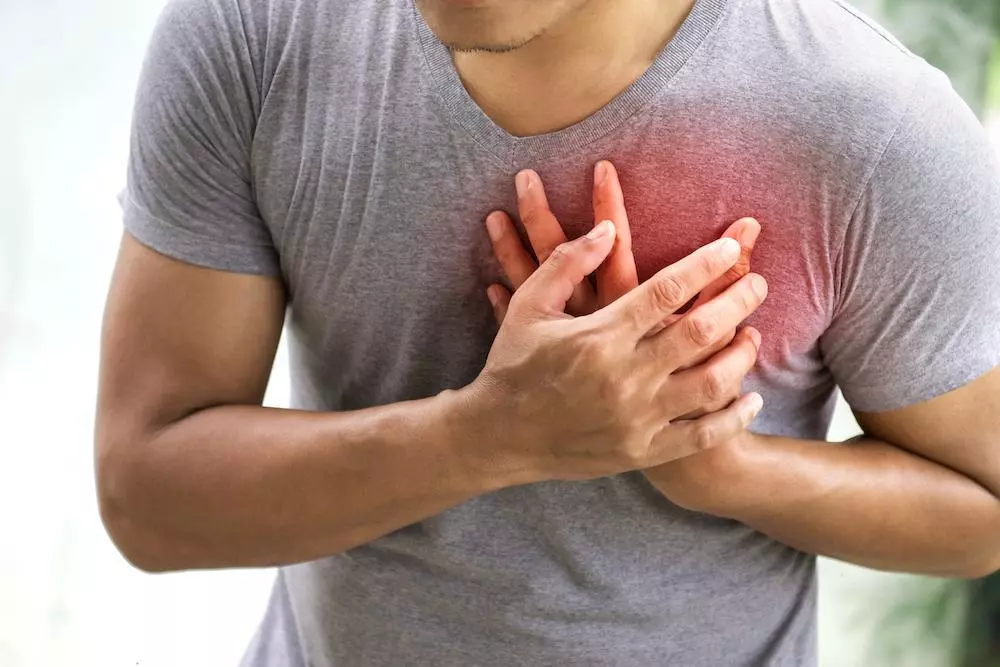

People who use cocaine regularly can experience long-term heart problems, such as an irregular heartbeat.
3. Brain damage

Cocaine use can cause irreversible brain damage and death.
4. Malnutrition

Cocaine use can lead to malnutrition, including vitamin deficiencies and anemia.
Is there a Test for Cocaine?
Many tests detect cocaine in the body, including blood, urine, saliva and hair tests. The most common ways to test for cocaine are urinalysis and a blood test.
Blood test: If you get tested for cocaine, they will likely use a blood test. A blood test can detect cocaine in your system within 48 hours of use.
Urine test: A urinalysis is the most common test to detect cocaine. It can detect cocaine within 72 hours of use.
Hair test: A hair test can detect drugs in your hair for up to 90 days. It’s the most accurate way to determine if you’ve used cocaine.
Bottom Line:
Cocaine is an extremely powerful stimulant that causes a fast but brief activation of dopamine in the brain. Dopamine is one of our feel-good neurotransmitters, and it plays an important role in regulating our emotions, pleasure response and motivation to take action to meet needs.
When we experience something rewarding (like taking a sip from our favorite coffee mug), dopamine receptors activate in order to alert us to take action again by keeping the coffee mug nearby so we can drink from it again soon.
Source –


