A Guide to Arrhythmia: Symptoms, Causes and Treatment 2022
When your heart beats too fast, too slow or erratically, it is one of the most common complications of coronary artery disease and can lead to serious health problems if not treated promptly. Arrhythmia is a type of abnormal heartbeat rhythm that may result in an irregular pulse rate and different types of cardiac arrhythmias.
Arrhythmias are often benign but can be a warning sign for more serious heart conditions. The prevalence of this condition increases with age and other factors such as genetics, high blood pressure, diabetes, and smoking. Let’s take a look at some useful information on this topic.
What is Arrhythmia?
Arrhythmia is an abnormal rhythm of the heartbeat. When your heart rate is too fast, too slow, or erratic, you could have an arrhythmia. Arrhythmias can cause palpitations, shortness of breath, dizziness, fainting, chest pain, and fatigue. Get a quick overview of arrhythmia, its symptoms and treatments. Arrhythmia is a type of abnormal heartbeat rhythm that may result in an irregular pulse rate.
It’s also known as dysrhythmia, irregular heartbeat, or abnormal heart rhythm. Abnormal heartbeats can happen because of a change in the electrical signals that make your heartbeat. Arrhythmia is often a sign of a bigger health problem, such as coronary artery disease, but it can be treated.
How is Arrhythmia Diagnosed?
Arrhythmia is diagnosed by taking a medical history, performing a physical examination and analyzing the heart rhythm (electrocardiogram or ECG). A doctor may also order imaging tests, blood tests or electrochemical studies. An ECG is a test that records the heart’s electrical activity to help diagnose arrhythmias.
During this test, pads with small electrodes are placed on the chest, arms or legs. The electrodes are attached to a machine that records your heart’s electrical activity.
Symptoms of Arrhythmia
1. Palpitations
A sensation of fluttering or pounding in the chest.
2. Shortness of Breath
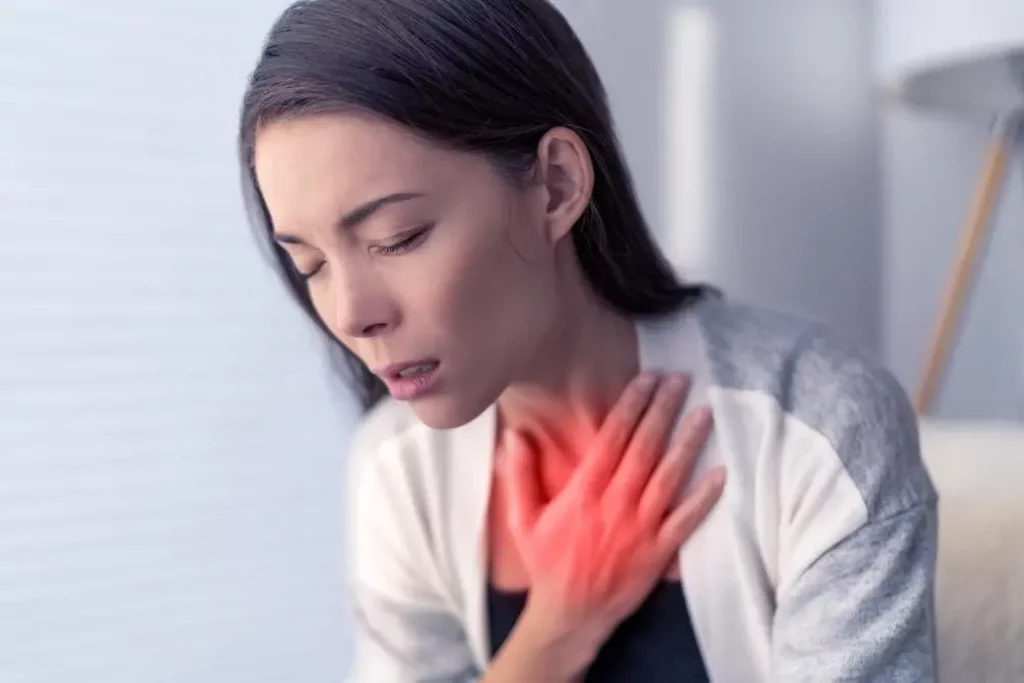

May be caused by heart rhythm disorders, disorders of the blood vessels in the lungs, and pulmonary embolism.
3. Dizziness
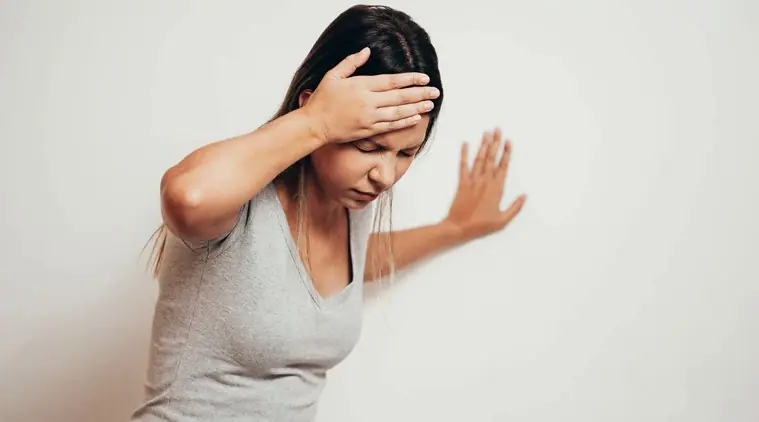

May be caused by low blood pressure with orthostatic hypotension or an arrhythmia.
4. Fainting
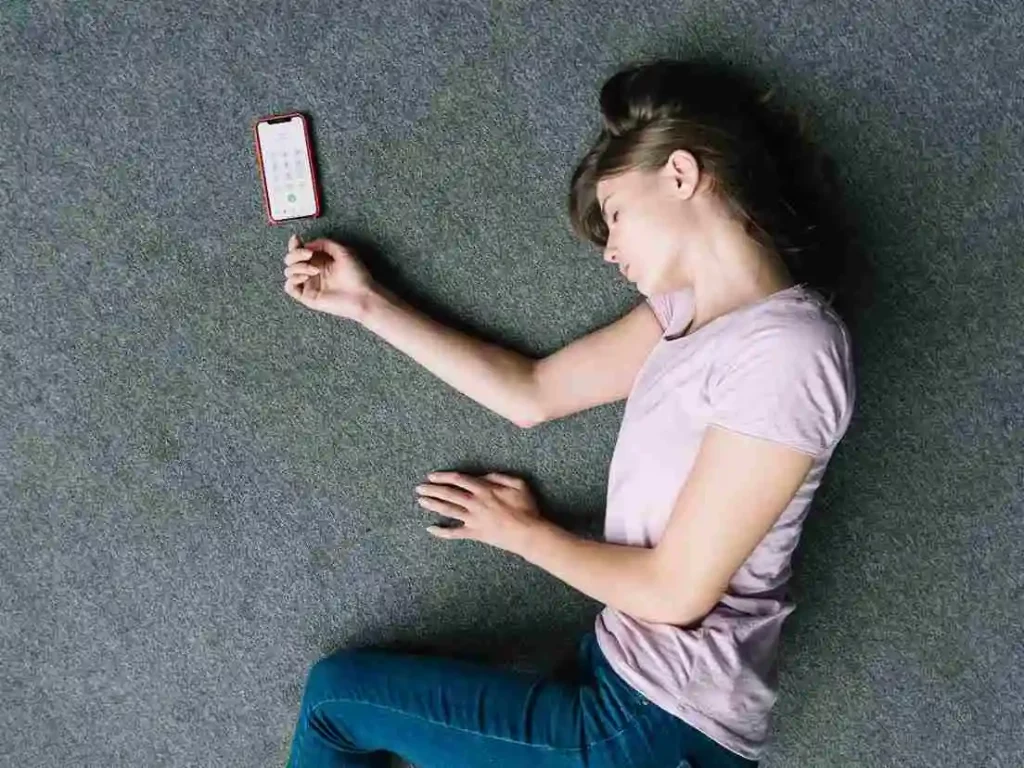

Can be triggered by an abnormal heart rhythm, disorders of the blood vessels, and anxiety.
5. Chest Pain
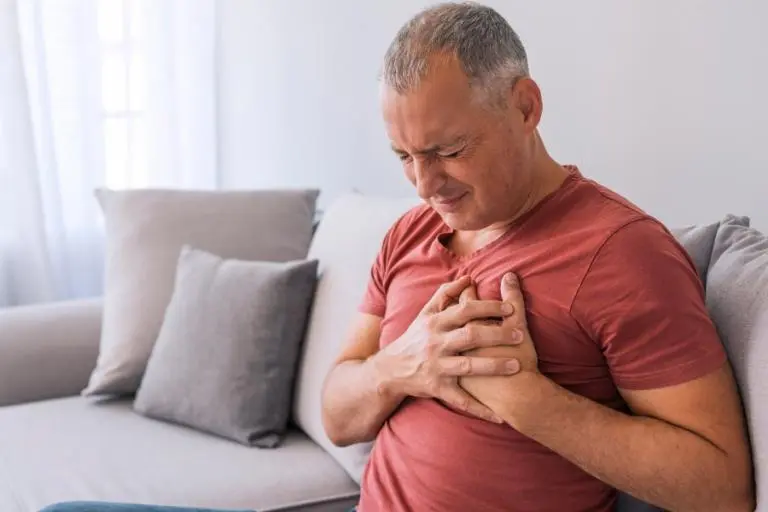

May be caused by coronary artery disease, aortic stenosis, and pericarditis.
Causes of Arrhythmia
Most commonly, arrhythmia is caused by coronary artery disease, a condition where plaque builds up in the arteries that supply blood to the heart. Other conditions including can also trigger rhythm disorders.
- Genetic mutations: A few genetic mutations are known to cause cardiac arrhythmias.
- Heart valve abnormalities: A heart valve abnormality may lead to the backflow of blood through the valve into your heart, disrupting your heart rhythm.
- Conditions that may cause heart inflammation, such as infections and autoimmune diseases: Infection and inflammation can trigger electrical abnormalities in the heart, leading to arrhythmias.
- Structural abnormalities: Abnormalities in the size and shape of the heart, such as a hole in the heart or hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, may disrupt the electrical signals that make your heartbeat.
- Heart muscle disorders: Diseases that affect the heart muscle, such as cardiomyopathy, can disrupt the electrical signals that make your heartbeat.
Treatment for Arrhythmia
Treatment will be customized according to the severity of the arrhythmia and other health conditions associated with it. Most arrhythmias do not require treatment but are monitored instead. Medications or implantable devices may sometimes be used to treat arrhythmias. Let’s look at some of the treatment options for arrhythmia.
- Medications: Arrhythmia can be treated with antiarrhythmic drugs or a combination of medications.
- Ablation: A procedure to destroy or damage heart tissue to treat arrhythmias.
- Pacemaker: A device that uses electrical impulses to control your heart rhythm.
- Implantable cardioverter defibrillator: A device that monitors your heart rhythm and delivers an electric shock if you risk a life-threatening arrhythmia.
- Surgical procedures: Open-heart surgery, endocardial surgery, and cardiac ablation may be required for severe arrhythmias.
Conclusion: Prevention of Arrhythmia
Arrhythmia is a condition where the heart beats too slowly or too quickly or where its beat is irregular. Many people experience arrhythmia at some point in their lives, but it does not always lead to more serious heart problems. If you experience any arrhythmia symptoms, you should see your doctor. There are a number of treatments available that can help control arrhythmia, and they can also help prevent it from getting worse.


