What is ALS (Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis)? Causes & Treatment 2022
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), also known as Lou Gehrig’s disease, is a progressive neurodegenerative condition that affects motor neurons in the brain and spinal cord. It causes weakness and eventual paralysis in the patient. There are almost 20 types of ALS, with type-specific subtypes.
The most common form is sporadic ALS, which represents 90% of all cases. There is no known cause of sporadic ALS, but there are certain risk factors that raise your risk of developing it. Other types include juvenile-onset ALS, familial or inherited ALS, or gene-drive mutations. Listed below are some facts about this disease:
What are the Causes of ALS?
ALS is a degenerative disease of the nervous system that is thought to be caused by damage to specific nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord. The damage is caused by the death of motor neurons, the cells responsible for sending instructions from the brain to muscles. The death of these motor neurons leads to muscle weakness and difficulty moving, problems with swallowing and breathing, and also affects sensation and speech.
The disease spreads in a pattern that mimics the spread of a fire from the bottom up. The causes of this condition are not known. However, a few factors have been linked to an increased risk of developing ALS, including genetics, smoking, and head trauma.
How is ALS Diagnosed?
ALS is a diagnosis of exclusion, meaning that if you have the symptoms, it has to be the only possible diagnosis. It is usually diagnosed by a neurologist after a detailed examination and after ruling out other diseases with similar symptoms.
The neurologist will ask about your symptoms and your medical history, perform a physical exam, and order blood tests and imaging scans to rule out other conditions. A lumbar puncture, also known as a spinal tap, may also be done to collect a sample of cerebrospinal fluid from the spinal cord, which can help rule out other conditions.
Risk Factors of ALS
- Age – ALS is most commonly diagnosed between the ages of 60 and 70. However, it can affect people of all ages, even children.
- Gender – Men are more likely to develop ALS than women, with the male-to-female ratio being about 10 to 1.
- Genetics – A small percentage of people with ALS have an inherited genetic mutation that causes their disease.
- Diet – A low-calorie diet and low levels of vitamin B have been associated with an increased risk of ALS.
- Smoking – Smokers are two to three times more likely to get ALS compared to non-smokers.
- Exposure to toxins – Exposure to heavy metals and pesticides has been linked to an increased risk of developing ALS.
Symptoms of ALS
The most common and early symptoms of ALS are:
- Weakness in the limbs or muscles of the face – The muscles that control eye movement, chewing and swallowing may be affected.
- Slurred speech: This can be due to weakness in the muscles that control the tongue.
- Problems with walking: Walking problems are typically caused by leg weakness.
- Trouble picking things up: Weakness in the hand muscles can make it difficult to grasp and lift things.
- Atrophy: The muscles in the arms, legs, and face can start to shrink as the disease progresses.
Treatments and Management of ALS
There is no cure for ALS, and there are no effective treatments that can slow down the progression of the disease. The goals of treatment are to improve the quality of life of the patient, manage pain, and prevent other complications.
1. Speech Therapy

This can help treat speech problems caused by ALS, such as slurred speech or trouble swallowing.
2. Physical Therapy
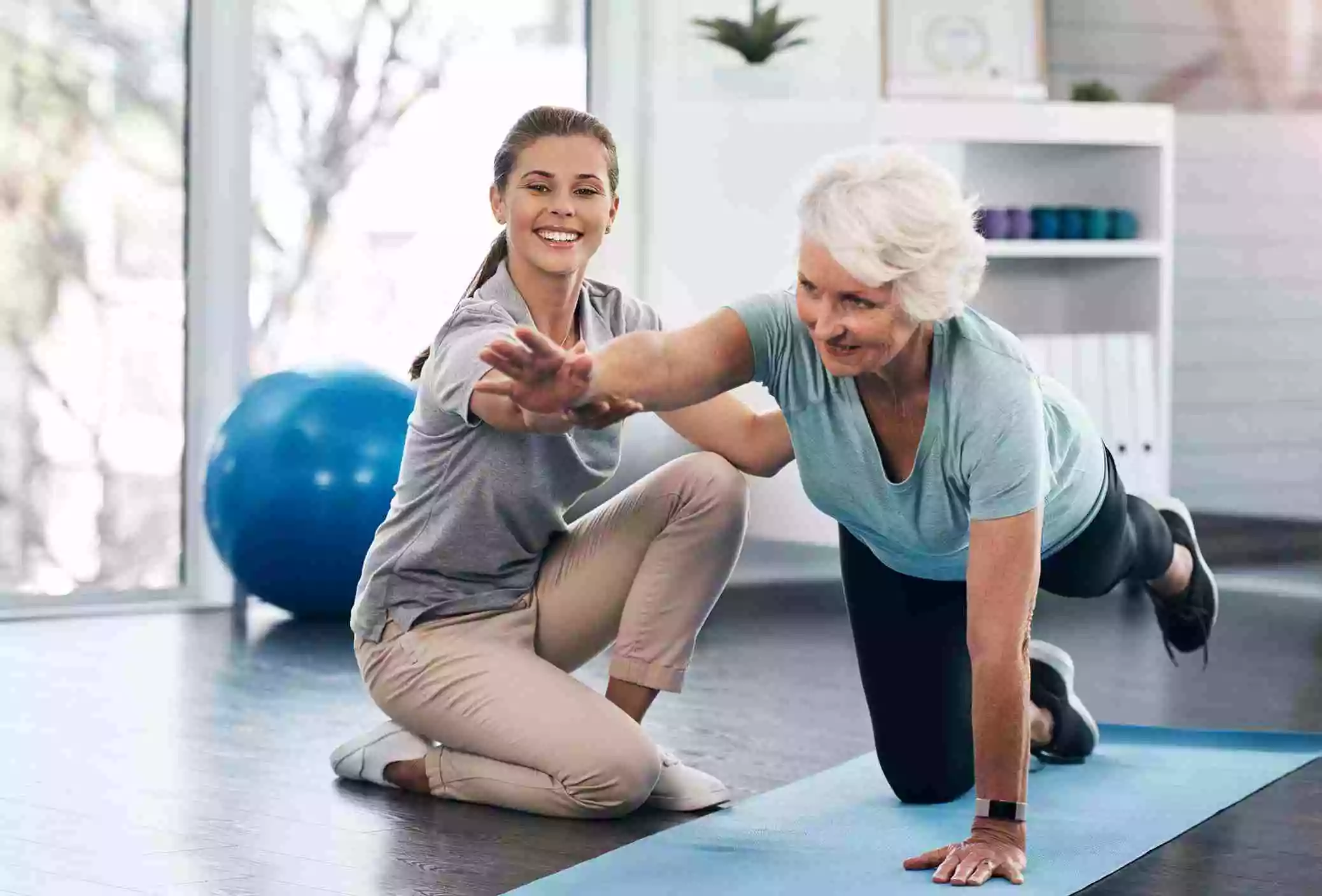

Physical therapy can help maintain strength in muscles that are affected by ALS, as well as help manage any pain caused by the disease.
3. Respiratory Support
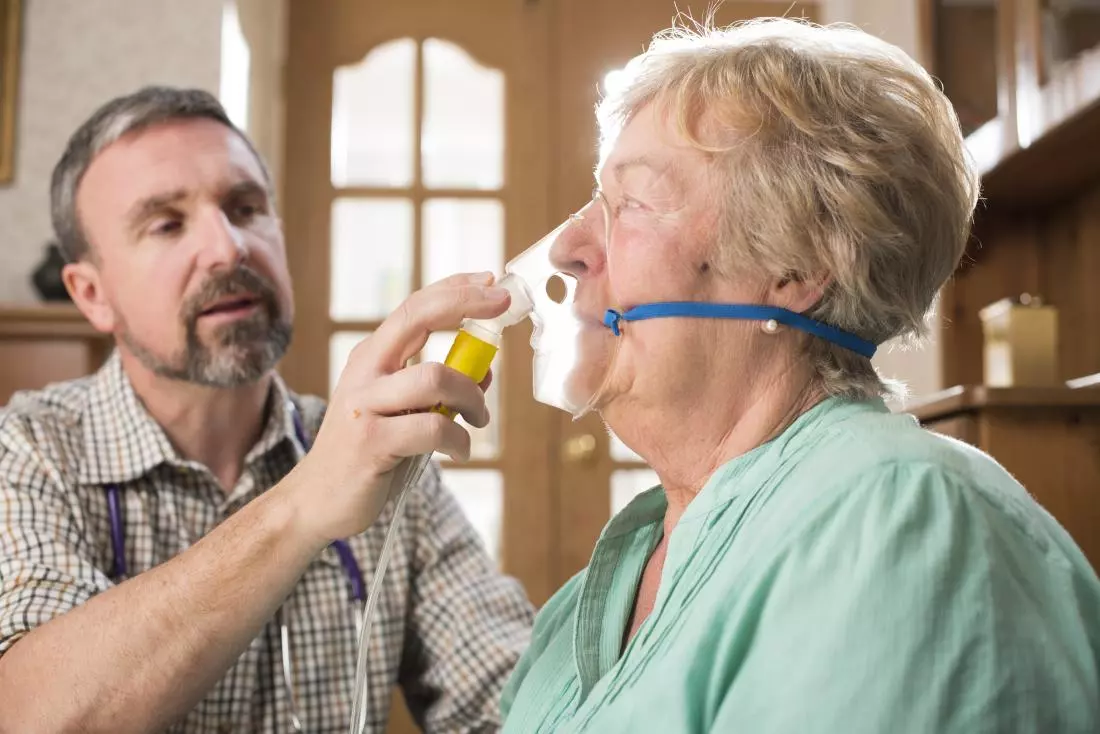

This can help people with ALS manage and prevent breathing problems caused by the disease.
4. Diet Modification

Eating a balanced diet can help manage symptoms of ALS, such as weight loss, fatigue, and muscle cramps.
5. Behavioral Therapy

This can help treat anxiety, stress, and depression related to ALS.
6. Medication
Medication may be prescribed to treat symptoms of ALS, such as pain and muscle cramps.
Conclusion
ALS is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder that affects motor neurons in the brain and spinal cord. It causes weakness and eventual paralysis in the patient. There are almost 20 types of ALS, with type-specific subtypes. The most common form is sporadic ALS, which represents 90% of all cases. There is no known cause of sporadic ALS, but there are certain risk factors that raise your risk of developing it.
Other types include juvenile-onset ALS, familial or inherited ALS, or gene-drive mutations. The causes of this condition are not known. However, a few factors have been linked to an increased risk of developing ALS, including genetics, smoking, and head trauma. The most common early symptoms of ALS are weakness in the limbs or muscles of the face, slurred speech, problems with walking; trouble picking things up; and atrophy.
Source –


